安全衛生情報センター
(別紙)
PFACに係る情報
名称:3-クロロ-1,1,2,3,3-ペンタフルオロ-1-プロペン
別名:パーフルオロアリルクロリド
CAS番号:79-47-0
化学式:CF2=CF-CF2Cl
構造式: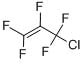

分子量:166.48
物理化学的性状:常温では無色の気体
沸点:約8℃
引火点:─
融点:約-140 ℃
用途:試験研究以外の情報なし
- 有害性情報:
- ヒトにおいて吸入、経口、経皮吸収により高い毒性を示す
- ばく露により、肺の刺激、胸痛と浮腫を起こし、致死性となりうる
- LCLO=27 ppm(最小致死濃度)(ラット)
- TCLO=5.4ppm(最小毒性量)(ラット)
【毒性試験】 3-chloropentafluoropropene(以下「PFAC」という。)は致死濃度が27ppm程度という非常に毒性の強 いガスである。雄ラットを用いて亜慢性毒性試験が行われている。1群10匹のラットを0、0.5、1.5、5.4 ppmのPFACを含む空気に1日6時間、週5日間で2週間ばく露し、ばく露終了時、及び13日後に、尿検査、臨 床化学的検査及び病理組織学的検査を行った。 ばく露中に、5.4ppm群のラットは、唾液分泌過多、鼻と口からの赤色の分泌液、呼吸速拍、呼吸困難など の症状を示した。この群のラットは有意な体重減少も示した。10回のばく露終了後に、1.5及び5.4ppm群 では赤血球容積とヘモグロビン濃度の増加が認められた。また、5.4ppm群では、ヘマトクリットの増加、 アルカリ尿があり、肺は大型化と質量の増加を示し、肺胞組織の急性炎症、出血、繊維性組織による置換 などを伴っていた。13日後には、肺の急性炎症は著しく改善し、軽度の肺胞繊維化を示す限局巣を残すの みだった。この時期にはその他の所見は認められなかった。PFACばく露による著しい影響は肺に対するも のであり、5.4ppmへのばく露で発生した。 (原文) 3-chloropentafluoropropene (PFAC) is a highly toxic gas with an approximate Lethality concentration of 27 ppm. Subchronic toxicity was evaluated in male rat. Groups of 10 rats were exposed 6 hours/day, 5 days/week for 2 weeks to atmospheres containing either 0, 0.5, 1.5, 5.4 ppm. Urinalysis , clinical chemistry and pathologic evaluations were performed at the end of the exposure period and 13 days later. During exposure , rats in the 5.4 ppm group exhibited salivation, dry red nasal and oral discharges , and rapid and labored breathing. Rats in this group also had significant body weight depression during the exposure period. Following 10 exposures , rats 1.5 and 5.4 ppm groups had increased red cell , mass and increased hemoglobin concentrations. Rats exposed to 5.4 ppm also had increased hematocrits , more alkaline urine , and enlarged , heavy lungs with acture inflammation of alveolar tissue , hemorrhage , and replacement by fibrous connective tissue. Thirteen days later there was a marked reduction of acture inflammation in the lungs with only focal areas of slight alveolar fibrosis. Other changes were absent at this time. The significant effect of exposure to PFAC was on the lungs and it occurred at a concentration of 5.4 ppm. 出典:Abstracts of the 1984 Annula Meeting,E.F.Stula,The Toxicologist Vol.4,Pg.66.1984, 【症例報告】 Fatal Chemical Pneumonia from 1,1,2,3,3-Pentaf luoro-3-chloropropene in an Unmarked Gas TankMichael Thun and Renate D. Kimbrough 要約 回収された円筒タンク内の未確認ガスへのばく露により、労働者に致死性の化学物質による肺炎を引き起 こした。タンクの調査の結果、1,1,2,3,3-ペンタフルオロ-3-クロロプロペンと走り書きされた化学式が 疑わしい肺の刺激物として明らかになった。円筒タンクの回収による潜在的な危険が、それらを使用し又 は詰め替える個々の作業者にもたらされることを、この報告は指摘している。危険にさらされている集団 にはスキューバダイバー、レスキュー隊員、圧縮ガス産業の従事者が含まれている。 (原文)Abstract Fatal chemical pneumonia occurred in a worker following exposure to an unidentified gas in a salvaged cylinder. Inspection of the tank revealed a scrawled chemical formula for 1,1,2,3,3-pentafluoro-3-chloropropene , a suspected pulmonary irritant. The report underscores the potential hazards which salvaged cylinders pose to individuals who use or refill them. Thepopulation at risk includes scuba divers, emergency rescue personnel, and workers in the compressed gas industry. 出典:Clin. Toxicol. 1981 Apr;18(4):481-7.


